today lesson is gonna talk about heap ,tries ,hashing that will be explained by the lecturer pak sky.
Heap
In computer science, a heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property: If A is a parent node of B then the key (the value) of node A is ordered with respect to the key of node B with the same ordering applying across the heap.
There are 3 kind of heap
1.Max-heap
is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater than or equal to the values in the children of that node.The value of the root have to be greater than any other nodes.

2.Min-Heap
is a complete binary tree in which the value in each internal node is greater than or equal to the values in the children of that node.The value of the root have to be smallest than any other nodes.

Min-Max Heap
is a double-ended priority queue implemented as a modified version of a binary heap. Like a binary heap, a min-max heap is represented as a complete binary tree.

Heap Majorly has 3 operations
-Insert Operation
-Delete Operation
-Extract-Min (OR Extract-Max)/not discussed on today lecture.
Insertion:
1. Add the element at the bottom leaf of the Heap.
2. Perform the Bubble-Up operation.
3.All Insert operations must perform the bubble-up operations (do it recursively).
Bubble-up Operation:
1.If inserted element is smaller than its parent node in case of Min-Heap OR greater than its parent node in case of Max-Heap, swap the element with its parent.
2.Keep repeating the above step, if node reaches its correct position, STOP.

Delete Operation:
1.Find the index for the element to be deleted.
2.Take out the last element from the last level from the heap and replace the index with this element 3.Perform Sink-down.
Sink-Down Operation:
1.If replaced element is greater than any of its child node in case of Min-Heap OR smaller than any if its child node in case of Max-Heap, swap the element with its smallest child(Min-Heap) or with its greatest child(Max-Heap).
2.Keep repeating the above step, if node reaches its correct position, STOP.

Tries
also called digital tree and sometimes radix tree or prefix tree (as they can be searched by prefixes), is an ordered tree data structure that is used to store a dynamic set or associative array where the keys are usually strings. Unlike a binary search tree, no node in the tree stores the key associated with that node; instead, its position in the tree defines the key with which it is associated. All the descendants of a node have a common prefix of the string associated with that node, and the root is associated with the empty string. Values are not necessarily associated with every node. Rather, values tend only to be associated with leaves, and with some inner nodes that correspond to keys of interest. For the space-optimized presentation of prefix tree, see compact prefix tree.

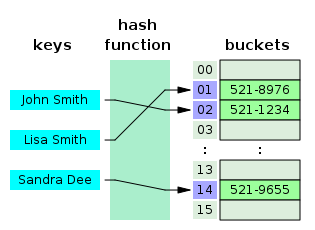
Hashing
a hash table (hash map) is a data structure used to implement an associative array, a structure that can map keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found.